Three-stage motors are a lot more productive than 1 section motors and are generally identified in programs requiring more than 7.5 horsepower. Even though the National Electric Code does not specify certain conductor colors for 3-stage existing, it is widespread to use black, pink and blue wires to identify traces L1, L2 and L3 respectively. The voltage cycle of every single line lags its predecessor by 100 and 20 degrees — L2 reaches its CZPT voltage following L1, and L3 reaches its CZPT voltage right after L2. Two wiring configurations, Wye and Delta, point out the wiring methods for a few-section motors. These instructions protect a dual voltage, 3-stage motor, the most widespread sort.
Action 1
Switch off the energy giving the circuit to be wired to the motor. A 3-phase motor need to be wired to a 3-section source.
Step 2
Open up the motor wiring box and identify the wires within. The 9 wires need to be labeled 1 via 9. Some motor sales opportunities are determined by color in this situation seek the advice of the motor documentation for lead identification.
Step 3
Examine the motor nameplate for wiring information. The nameplate will specify the motor voltages and could give specific wiring info. Several motors can be wired for a high and reduced voltage and for either Delta or Wye (at times known as Y or Star wiring). Wire the motor for the appropriate voltage to which you are connecting the motor.
Step 4
Make all wiring connections with wire nuts of the right dimensions for the conductors getting utilised and the number of conductors currently being related with each other. If there is a neutral wire in the conduit or cable supplying the motor, it is unused for the motor’s a few-phase wiring cap it with a wire nut. For instance, use a purple wire nut to join 2 12-gauge wires. Hold the bare ends of the conductors with each other and twist on a wire nut.
Stage 5
Swap any 2 line connections to reverse the motor rotation. For illustration, go provide line T1 to T2 and source line T2 to L1 and the motor will reverse route. You can buy motor control switches to attain this modify.
Wye Wiring
Stage 1
Make the connections for low voltage, 230-volt wiring. Connect motor sales opportunities 4, 5 and 6 with each other. Link motor qualified prospects 7 and 1 with the black L1 conductor. Hook up motor qualified prospects 8 and 2 with the red L2 conductor. Link motor prospects 9 and 3 with the blue L3 conductor.
Step 2
Make the connections for large voltage, 460-volt wiring. Hook up motor sales opportunities 6 and 9 together. Connect motor qualified prospects 5 and 8 with each other. Connect motor sales opportunities 4 and 7 together. Hook up motor CZPT 1 to the black L1 conductor. Hook up motor CZPT 2 to the pink L2 conductor. Hook up motor direct 3 to the blue L3 conductor.
Step 3
Join the ground wire to the motor’s ground terminal. Loosen the floor terminal screw, insert the floor wire into the terminal and tighten the screw firmly. Shut the motor’s wiring box.
Delta Wiring
Action 1
Make the connections for reduced voltage, 230-volt wiring. Connect motor qualified prospects 1, 7 and 6 to the black L1 conductor. Hook up motor prospects 2, 8 and 4 to the purple L2 conductor. Link motor sales opportunities 3, 5 and 9 to the blue L3 conductor.
Action 2
Make the connections for substantial voltage, 460-volt wiring. Join motor qualified prospects 9 and 6 collectively. Hook up motor sales opportunities 4 and 7 collectively. Connect motor prospects 8 and 5 with each other. Link motor lead 1 to the black L1 conductor. Join motor lead 2 to the purple L2 conductor. Connect motor lead 3 to the blue L3 conductor.
Phase 3
Join the floor wire to the motor’s floor terminal. Loosen the ground terminal screw, insert the floor wire into the terminal and tighten the screw firmly. Close the motor’s wiring box.
What Is a Gear Motor?
A gear motor is an electric motor coupled with a gear train. It uses either DC or AC power to achieve its purpose. The primary benefit of a gear reducer is its ability to multiply torque while maintaining a compact size. The trade-off of this additional torque comes in the form of a reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, proper gear technology and ratios provide optimum output and speed profiles. This type of motor unlocks the full potential of OEM equipment.
Inertial load
Inertial load on a gear motor is the amount of force a rotating device produces due to its inverse square relationship with its inertia. The greater the inertia, the less torque can be produced by the gear motor. However, if the inertia is too high, it can cause problems with positioning, settling time, and controlling torque and velocity. Gear ratios should be selected for optimal power transfer.
The duration of acceleration and braking time of a gear motor depends on the type of driven load. An inertia load requires longer acceleration time whereas a friction load requires breakaway torque to start the load and maintain it at its desired speed. Too short a time period can cause excessive gear loading and may result in damaged gears. A safe approach is to disconnect the load when power is disconnected to prevent inertia from driving back through the output shaft.
Inertia is a fundamental concept in the design of motors and drive systems. The ratio of mass and inertia of a load to a motor determines how well the motor can control its speed during acceleration or deceleration. The mass moment of inertia, also called rotational inertia, is dependent on the mass, geometry, and center of mass of an object.
Applications
There are many applications of gear motors. They provide a powerful yet efficient means of speed and torque control. They can be either AC or DC, and the 2 most common motor types are the 3-phase asynchronous and the permanent magnet synchronous servomotor. The type of motor used for a given application will determine its cost, reliability, and complexity. Gear motors are typically used in applications where high torque is required and space or power constraints are significant.
There are 2 types of gear motors. Depending on the ratio, each gear has an output shaft and an input shaft. Gear motors use hydraulic pressure to produce torque. The pressure builds on 1 side of the motor until it generates enough torque to power a rotating load. This type of motors is not recommended for applications where load reversals occur, as the holding torque will diminish with age and shaft vibration. However, it can be used for precision applications.
The market landscape shows the competitive environment of the gear motor industry. This report also highlights key items, income and value creation by region and country. The report also examines the competitive landscape by region, including the United States, China, India, the GCC, South Africa, Brazil, and the rest of the world. It is important to note that the report contains segment-specific information, so that readers can easily understand the market potential of the geared motors market.
Size
The safety factor, or SF, of a gear motor is an important consideration when selecting 1 for a particular application. It compensates for the stresses placed on the gearing and enables it to run at maximum efficiency. Manufacturers provide tables detailing typical applications, with multiplication factors for duty. A gear motor with a SF of 3 or more is suitable for difficult applications, while a gearmotor with a SF of 1 or 2 is suitable for relatively easy applications.
The global gear motor market is highly fragmented, with numerous small players catering to various end-use industries. The report identifies various industry trends and provides comprehensive information on the market. It outlines historical data and offers valuable insights on the industry. The report also employs several methodologies and approaches to analyze the market. In addition to providing historical data, it includes detailed information by market segment. In-depth analysis of market segments is provided to help identify which technologies will be most suitable for which applications.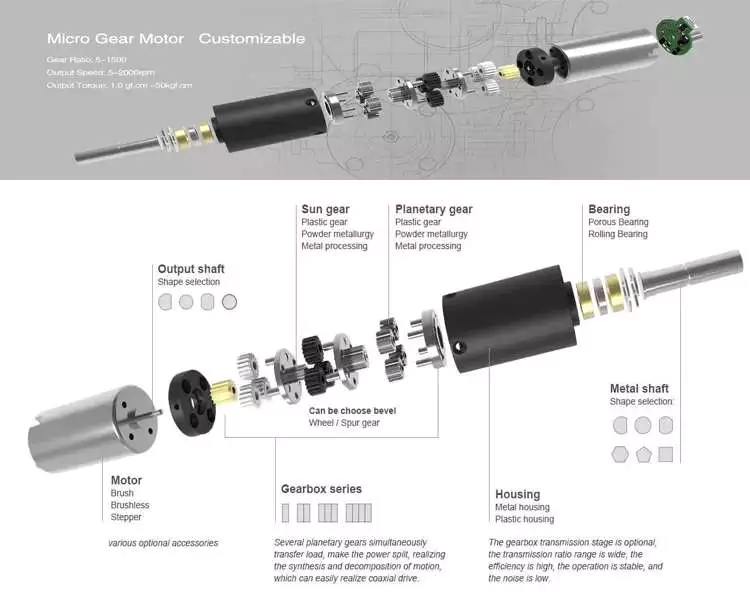
Cost
A gear motor is an electric motor that is paired with a gear train. They are available in AC or DC power systems. Compared to conventional motors, gear reducers can maximize torque while maintaining compact dimensions. But the trade-off is the reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, when used correctly, a gear motor can produce optimal output and mechanical fit. To understand how a gear motor works, let’s look at 2 types: right-angle geared motors and inline geared motors. The first 2 types are usually used in automation equipment and in agricultural and medical applications. The latter type is designed for rugged applications.
In addition to its efficiency, DC gear motors are space-saving and have low energy consumption. They can be used in a number of applications including money counters and printers. Automatic window machines and curtains, glass curtain walls, and banknote vending machines are some of the other major applications of these motors. They can cost up to 10 horsepower, which is a lot for an industrial machine. However, these are not all-out expensive.
Electric gear motors are versatile and widely used. However, they do not work well in applications requiring high shaft speed and torque. Examples of these include conveyor drives, frozen beverage machines, and medical tools. These applications require high shaft speed, so gear motors are not ideal for these applications. However, if noise and other problems are not a concern, a motor-only solution may be the better choice. This way, you can use a single motor for multiple applications.
Maintenance
Geared motors are among the most common equipment used for drive trains. Proper maintenance can prevent damage and maximize their efficiency. A guide to gear motor maintenance is available from WEG. To prevent further damage, follow these maintenance steps:
Regularly check electrical connections. Check for loose connections and torque them to the recommended values. Also, check the contacts and relays to make sure they are not tangled or damaged. Check the environment around the gear motor to prevent dust from clogging the passageway of electric current. A proper maintenance plan will help you identify problems and extend their life. The manual will also tell you about any problems with the gearmotor. However, this is not enough – it is important to check the condition of the gearbox and its parts.
Conduct visual inspection. The purpose of visual inspection is to note any irregularities that may indicate possible problems with the gear motor. A dirty motor may be an indication of a rough environment and a lot of problems. You can also perform a smell test. If you can smell a burned odor coming from the windings, there may be an overheating problem. Overheating can cause the windings to burn and damage.
Reactive maintenance is the most common method of motor maintenance. In this type of maintenance, you only perform repairs if the motor stops working due to a malfunction. Regular inspection is necessary to avoid unexpected motor failures. By using a logbook to document motor operations, you can determine when it is time to replace the gear motor. In contrast to preventive maintenance, reactive maintenance requires no regular tests or services. However, it is recommended to perform inspections every 6 months.

